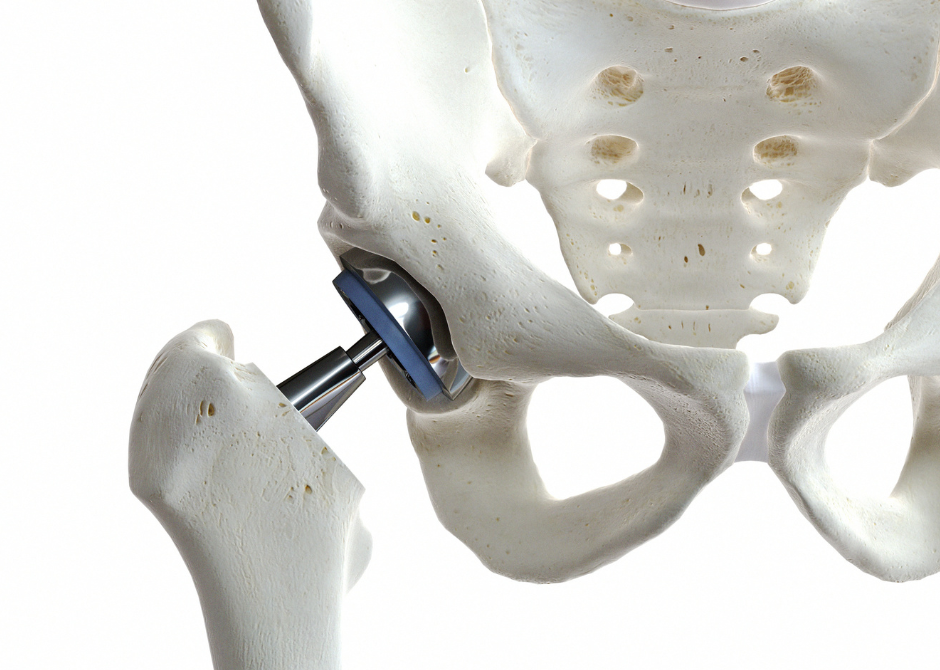
In recent years, many medical devices, including artificial joints, have been manufactured in Japan.
However, there may be many people who are considering manufacturing artificial joints but have questions such as "I want to know if it is possible to manufacture artificial joints by cutting" or "I want to know what to look out for during the cutting process.
In this article, we will discuss the advantages and cautions when manufacturing artificial joints by cutting.
Please refer to the following information on how to select a contractor for your project.
For more information about Taiga, click here.
Table of Contents
Cutting is the preferred processing method for manufacturing artificial joints
An artificial joint is an artificially manufactured joint used to replace a bone or joint that has lost function or function due to injury or disease.
Artificial joints are a technology originally developed in the United States, but in recent years many artificial joints have been manufactured and developed in Japan.
While prostheses must be customized to the person who will use them, they must also be manufactured with low cost and short delivery times in mind.
Therefore, cutting is the manufacturing method of choice for artificial joints.
Artificial joints are made of titanium, a highly biocompatible metal.
Cutting is performed by using machines such as NC lathes and machining centers to cut materials while machining, enabling stable manufacturing of artificial joints that require high precision.
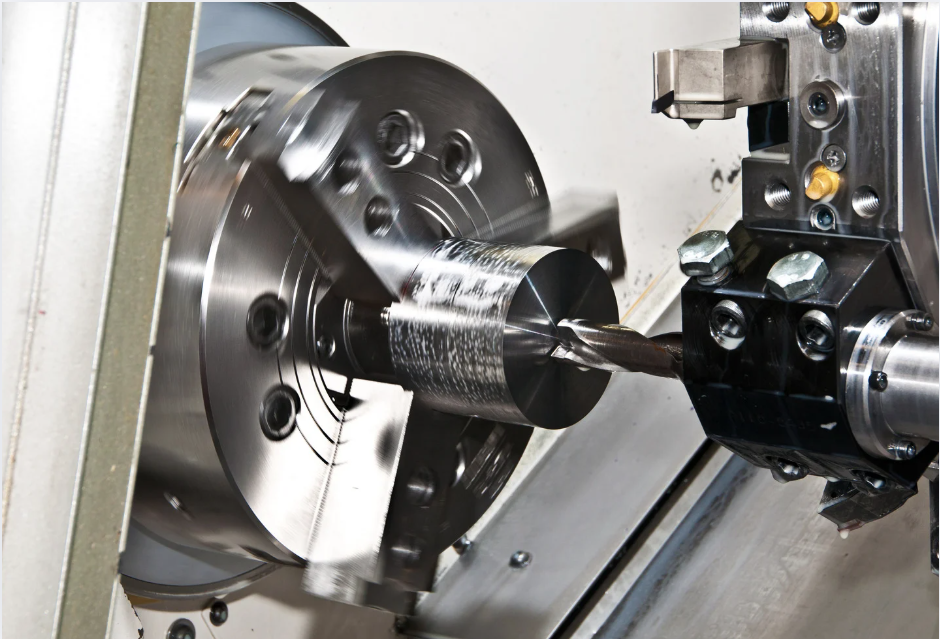

Advantages of Using Cutting Processes in the Manufacture of Artificial Joints
This section describes the specific advantages of using the cutting process in the manufacture of artificial joints.
High-precision finish can be expected.
Cutting is based on programs and 3D-CAD data, and the machine is computer-controlled.
Although it depends on the machine, micron-level control and surface roughness adjustment are also possible, making it suitable for machining precision equipment parts, semiconductor-related products, and other items requiring accuracy.
Cutting can be used to manufacture joint prostheses that require customization according to the person using the joint and the location of the joint, while maintaining high dimensional accuracy and specifications.
High degree of freedom of shape
Cutting is not limited by the thickness of the material as long as the machine can handle it.
In addition, because machining is performed based on programs and data, machining of complex shapes can be realized with maintained accuracy.
For these reasons, cutting is also suited to the manufacture of artificial joints, where customization is required.
Low cost and short delivery time
Products that require customization, such as artificial joints, inevitably tend to have longer manufacturing turnaround times and higher costs.
In this respect, cutting does not require molds as injection molding and other processing methods do.
This eliminates the time and expense of mold fabrication and shortens delivery time while also achieving low-cost manufacturing.
Cutting can also be an effective machining method when you are struggling to ensure customizability of artificial joints, short delivery times, and low costs.
Can be used with a variety of materials
Processing that uses molds, such as injection molding, has the disadvantage of accommodating only a limited range of materials because the material is melted, filled, and solidified in the mold.
On the other hand, with cutting, we can handle anything that can be shaved with a tool.
Not only plastics and resins, but also metals such as aluminum, iron, and stainless steel can be processed.
Of course, titanium, which is mainly used in artificial joints, can also be machined.
What is required for the cutting process of artificial joints
The cutting process for artificial joints must take into account different points from other product fabrication.
Specific points required for the cutting process of artificial joints will be explained.
High-precision finish tailored to the individual body
Artificial joints are manufactured according to the standard dimensions set by the manufacturer, and in many cases, the human body is now being adapted to the artificial joint.
It is predicted that as the need for artificial joints increases, they will be made to fit the size and shape of different joints in different individuals.
Therefore, precise dimensional control will be required to ensure that the size and shape of the product conforms to the person using it.
Even in cutting processes that can achieve high precision, it is important to maintain accuracy in dimensions and surface finish.
Must be able to meet medical device standards
Medical devices, including artificial joints, must be sufficiently safe and of high quality for use in the human body.
Unlike the cutting process for general products, it is necessary to establish a system that can manufacture artificial joints that meet the standards for medical devices.
For example, ISO 13485 is a standard intended to establish a quality management system for medical device manufacturers and organizations providing related services.
ISO 13485 has been adopted as an international standard that can demonstrate "the ability to provide medical devices that consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
In addition, "GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice)" has been established as a standard in accordance with ISO13485.
When cutting artificial joints, it is essential to meet the standards for medical devices, including ISO13485 and GMP compliance.
Inexpensive processing
As medical devices, joint prostheses must be manufactured with high precision and safety, and must also be cost-effective.
This is because the cheaper the prostheses become, the more people who need them can be supplied with them.
Cutting will need to be done with an eye toward cost reduction, such as more efficient manufacturing while maintaining conventional precision and safety.
Precautions in Cutting Artificial Joints
Although there are many advantages to manufacturing joint prostheses by cutting, challenges may arise in terms of material properties and technology during processing.
High degree of processing difficulty depending on the material used
In cutting, machining difficulty may increase depending on the material.
In particular, titanium, which is used as a material for artificial joints, is one of the hardest materials to cut and process.
It is important to request the cutting process of artificial joints to a highly skilled supplier who can select appropriate tools and set cutting conditions for titanium cutting.
Not suitable for mass production
Cutting process is a process of machining materials, which inevitably takes time to process.

In addition, the cost of materials tends to be high because it is difficult to reuse scraped materials.
Cutting allows for quick delivery and low-cost production of a small number or one-off items, but is not suitable for mass production.
Product workmanship is prone to variation.
Cutting is a machining process that is prone to wear on the blade and to differences in dimensions and surface roughness.
In addition, chips generated by cutting adhere to the tool, causing wear of the cutting tool and loss of cutting accuracy.
Even products made of the same material are prone to variations in processing workmanship, making them unsuitable for the repeated production of the same item.
In order to maintain product quality and standards, tool maintenance and control of machining conditions are required for each machining operation.
Requires technical skills of workers
To achieve high-precision cutting, it is necessary to select appropriate tools and adjust cutting conditions.
Even if cutting is performed under the same conditions, the accuracy of the cutting process will be lower depending on the skill and knowledge possessed by the operator.
Workers with a proven track record and high technical skills are essential, especially in the cutting process of artificial joints that process titanium.
How to choose a supplier for cutting artificial joints
Achieving ideal processing in the manufacture of artificial joints requires advanced technology and specialized knowledge.
Choose a supplier that is not only capable of cutting artificial joints, but also has experience in many cutting processes.
If the website includes specific examples of prosthesis fabrication, it is proof that the company has high technology.
In addition, since artificial joints are medical devices, it is important to choose a supplier that processes them to ensure their quality and safety as a product.
Choose a supplier that has a production system for medical devices that is ISO 13485 certified, complies with GMP, and conducts its own inspections.
Summary
We have explained the points and advantages of cutting for the manufacture of artificial joints, as well as points to be noted in the cutting process for artificial joints.
The need for artificial joints is expected to increase in the future, and low-cost, quick-delivery fabrication by cutting is also attracting attention.
It is important to choose a supplier with high technology and a proven track record in order to achieve the manufacture of prostheses that are highly accurate and can guarantee safety.
If you are considering manufacturing components in the medical field, please contact us!Taiga."Taiga is a free service that allows you to consult with experienced contractors.
We can efficiently proceed with the development of difficult or new parts, small-lot production, prototyping, and mass production while keeping costs low.
For more information about Taiga, click here.
 0120-987-742
0120-987-742


