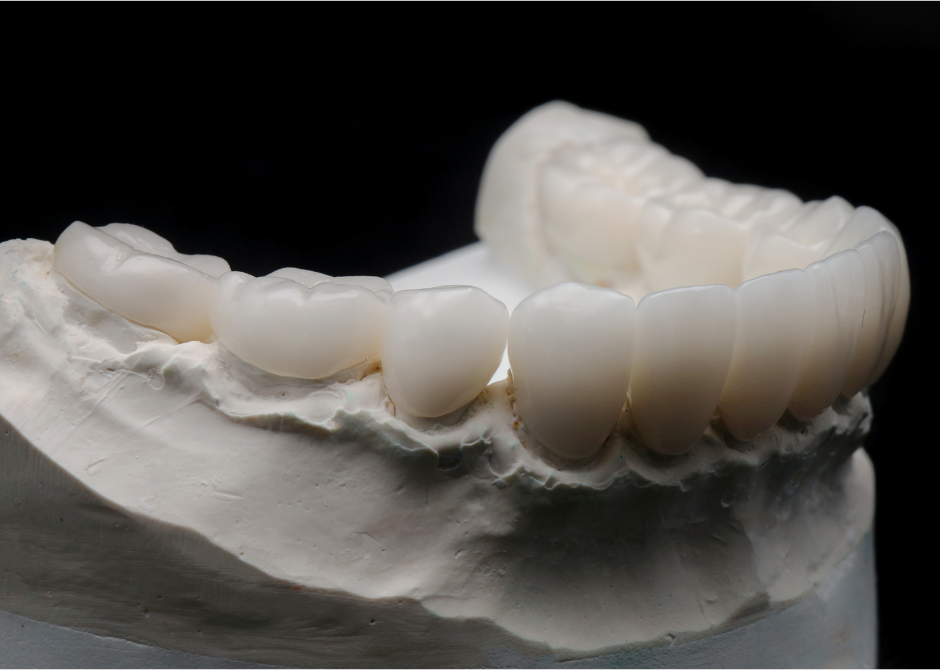
In recent years, 3D printing has been attracting attention as a way to manufacture more precise components using ceramics.
However, I have heard a lot of questions like, "Are ceramics compatible with 3D printing?" Are there any precautions to take when 3D printing?" Many people may have questions such as "Is 3D printing compatible with ceramics?
In this article, we will discuss the features and benefits of 3D printing of ceramics and the main methods of modeling.
We also introduce how to choose a 3D printing vendor for your 3D printing needs.
For more information about Taiga, click here.Table of Contents
What is ceramic 3D printing?
Ceramic is an inorganic compound material consisting of porcelain, ceramics, glass, cement, etc.

In addition to its superior strength, corrosion resistance, heat resistance, and electrical insulation properties, it is used as a material for a wide variety of parts and products because of its light weight.
Ceramics have the advantage of being able to combine a wider range of elements than resins or metals, making them easier to apply.
There are various methods of processing ceramics, but in recent years, ceramic 3D printers, which support 3D printing of ceramics, have been attracting attention.
Advantages of Ceramic 3D Printing|Why is it attracting attention now?
With ceramic 3D printers, the material, ceramic, is layered rather than shaved.
This has made it possible to form products with complex shapes and hollow structures that could not be fabricated by cutting and other conventional machining methods.
Also, since molds are not required, there is no time or cost for mold fabrication, and delivery time and cost can be reduced while maintaining high accuracy of finished products and prototypes.
In recent years, not only major companies but also small and medium-sized enterprises and start-ups have introduced 3D printers, and the demand for ceramic-compatible 3D printers is increasing every year.
The main methods of ceramic 3D printer modeling
Ceramic 3D printers offer a variety of modeling methods, each with different advantages and disadvantages.
The following is a step-by-step explanation of the main molding methods of ceramic 3D printers.
Laser melting method (SLM)
The laser melting method is a method in which powdered ceramics are melted by irradiating them with a laser and then layered to form a model.
Since the modeling is done using a thin laser, parts with complex shapes can be made with high precision.
However, it should be noted that there are only a few types of powdered ceramics that can be used, and the range of material selection is limited.
In recent years, there has been a lot of development and research into powder ceramics that are compatible with the laser melting method, but keep in mind that there are still not many options available.

Binder jet method
The binder jet method is a method in which a binder, which is a bonding agent for photo-curable resin, is injected from an inkjet head, and the binder is modeled while being layered.
Infrared lasers harden ceramic powders, allowing for the creation of complex shapes and coloring of materials.
The fast molding speed and the absence of the need for support materials enable efficient molding.
Note, however, that the strength of the molding is somewhat low and the surface remains powdery.
Major industries and fields where ceramic 3D printing is used
This section describes the main industries and fields where ceramic 3D printing is used.
Automotive
In the automotive industry, the high strength and lightweight properties of ceramics are being utilized to reduce the weight of automobiles.
Ceramics reduce the weight of the vehicle body, thereby improving fuel efficiency and making it carbon neutral.
In the future, it is expected to be used in automobile engine parts, taking advantage of its high heat resistance.

Aerospace
The high strength, corrosion resistance, heat resistance, and wear resistance of ceramics are utilized as components for aircraft and space rockets.
For example, ceramics are used in rocket engines, nozzles, and other parts and bodies.
Medical Field
In addition to its high chemical resistance, ceramic is a material that is not easily allergic.
For this reason, it is widely used in dental implants, artificial joints, and other medical devices such as gauges and pumps for the heart.
Medical devices require high dimensional accuracy to match the body of the person using them, and this is an area in which 3D printing of ceramics is particularly promising.
electronic parts (components)
In the field of electronic components, there is a growing need for the manufacture of ceramic components to reduce the weight and size of devices.
The combination of lightweight ceramics and 3D printed hollow structures makes it possible to produce electronic components that are both strong and lightweight.
Decoration industry
Depending on the 3D printing method of ceramic modeling, coloring of the material may also be possible.
With 3D printing, colored ceramic materials can be sculpted into complex shapes, which are used in a variety of settings in the decorative industry.
Cautions in Ceramic 3D Printing
While there are many advantages to ceramic 3D printing, there are also some things to keep in mind.
Shrinks when raw materials are heated
Ceramic has the property of becoming denser and harder when heated, which causes shrinkage of the raw material.
Shrinkage also occurs during modeling with a 3D printer, making high-precision modeling difficult depending on the modeling method.
It will be necessary to select a modeling method that can emphasize accuracy, such as the laser melting method.
Cracks due to processing after molding
In 3D printing of ceramics, cracking may occur during post-processing after modeling.
Cracking can be caused by a variety of reasons, including rapid temperature changes during heating, concentration of heat in one area, resin remaining inside the molded object, raw material formulations, and molding conditions.
To prevent cracking in post-processing, it is necessary to select appropriate raw materials, set molding conditions, and select an efficient method for removing the resin remaining inside.
How to choose a vendor for ceramic 3D printing
When choosing a vendor for ceramic 3D printing, keep the following points in mind.
Is there a 3D printer facility that can handle ceramics?
Even suppliers that can handle resin and metal 3D printing may not be able to handle ceramic 3D printing.
First, check to see if 3D printing of ceramics is supported.
Do you have extensive experience in ceramic 3D printing?
3D printing of ceramics requires the selection of appropriate modeling conditions and materials. If a contractor without the know-how is commissioned, there is a risk of shrinkage due to heat and cracking during post-processing.
For this reason, it is recommended that you request 3D printing of ceramics from a company with extensive experience in this field.
Cost and turnaround time for 3D printing
The costs and turnaround time incurred in 3D printing vary from vendor to vendor.
Even if the same ceramic material is used for modeling, be sure to commission a company that you are satisfied with in terms of cost and turnaround time.
Summary
Along with the features and merits of ceramic 3D printing, we explained the cautions and issues to consider when requesting ceramic 3D printing.
Ceramic is a material used in the automotive and medical industries, and in recent years, 3D printing technology has been attracting attention.
When requesting 3D printing of ceramics, be sure to choose a vendor with a good track record and technology.
If you are considering manufacturing components using ceramics, please contact us.Taiga."Please make use of the following
Taiga is a free service that allows you to consult with experienced contractors.
We can efficiently proceed with the development of difficult or new parts, small-lot production, prototyping, and mass production while keeping costs low.
For more information about Taiga, click here.
 0120-987-742
0120-987-742