3D printing technology is a revolutionary manufacturing method that allows for the free design of internal structures of products.
It enables efficient production of complex-shaped items and significantly enhances the speed and flexibility of product development.
In this article, we will thoroughly explain the various 3D printing methods for resin, the characteristics of resin materials, and key points to consider when selecting materials.
For more information about Taiga, click here.Table of Contents
What is 3D printing of resin?
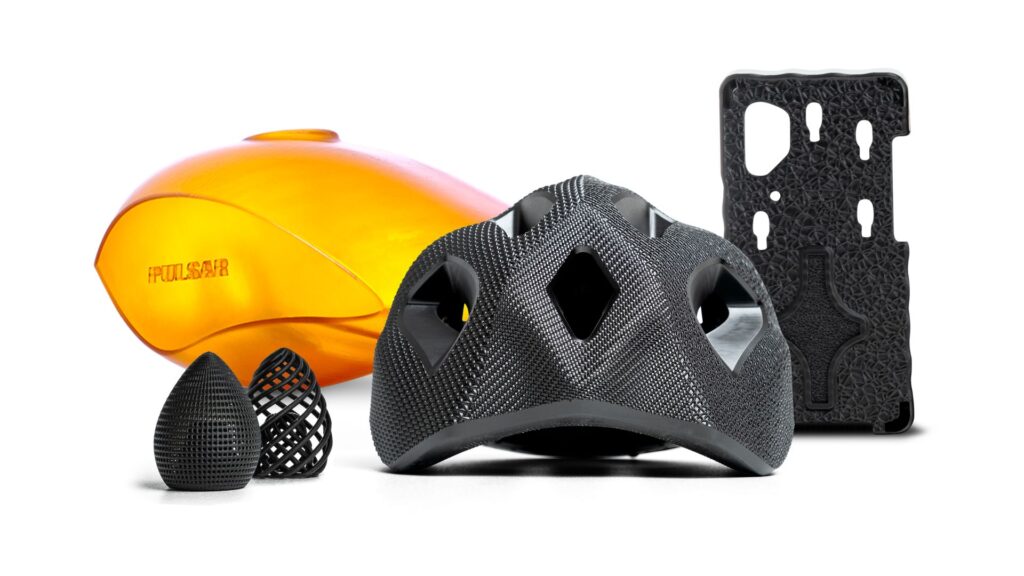

Resin 3D printing is a manufacturing technology that creates three-dimensional objects by layering resin materials based on digital data.
Complex shapes and structures can be modeled with high precision, and the modeling time and cost are superior to those of conventional manufacturing methods.
Because it can be used with a variety of materials, including metals and carbon as well as resins, it is used in a wide range of fields, including aerospace, automotive, and medical.
Main molding methods in resin 3D printers
This section describes the main molding methods of resin 3D printing and the characteristics of each.
Thermal melting lamination (FDM) method
The FDM method is a technology in which thermoplastic resin filaments are heated and melted by a nozzle and stacked in layers for modeling.
Because thermoplastic resins such as ABS can be used, its strength lies in its ability to produce moldings with high strength and heat resistance.
We also support a variety of materials such as engineering plastics and super engineering plastics.
On the other hand, it has the disadvantage that lamination marks are easily visible, and is not suitable when a smooth surface is required.
The FDM method is suitable for manufacturing prototypes, jigs, and tools in the manufacturing industry, as well as for molding final products that require high strength.
Rapid prototyping
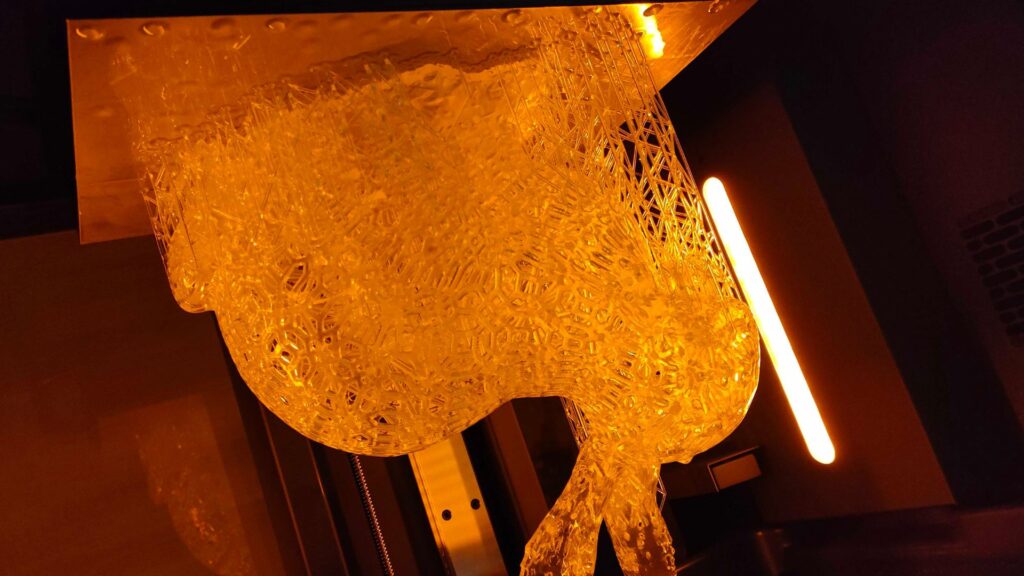

The optical molding method is a technology in which liquid light-curing resin is cured by irradiating it with ultraviolet light.
It is capable of high-precision modeling and smooth surface finish.
It is suitable for manufacturing precision parts and complex shapes, and is widely used in the medical field and jewelry manufacturing.
On the other hand, keep in mind that there are some disadvantages, such as deterioration caused by sunlight and the time and effort required for post-processing.
There are two types of optical fabrication methods: SLA and DLP, each of which has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Ink-jet method
The inkjet method is a technology in which liquid photocurable resin is injected as fine droplets and cured by ultraviolet light.
Multi-material modeling, which allows multiple materials to be used simultaneously, is possible, and full-color modeling is also possible.
Recently, in addition to being able to use transparent clear materials, some models can reproduce the texture of rubber or print directly on cloth or leather.
Because of its ability to create highly detailed and expressive modeling, it is suited for manufacturing precision parts and products that require design quality.
However, it should be noted that the strength and durability of this method is inferior to the FDM method, and there are issues such as degradation due to sunlight.
Binder jet method
The binder jet method is a printing technology in which adhesive is sprayed onto powdered materials to solidify them.
The binder jet method is characterized by its high molding speed and ability to produce large moldings.
Mainly made of plaster powder or resin powder, it is suitable for applications where design is more important than strength, such as architectural models and artwork production.
Full-color modeling is also possible by using colored bonding agents.
Unused molding material can be reused, making it cost-effective and eliminating the need for support material removal.
On the other hand, it has the disadvantages of a rough surface and low durability, and safety measures related to handling and removal of the powder are necessary.
Main resin materials used in 3D printing
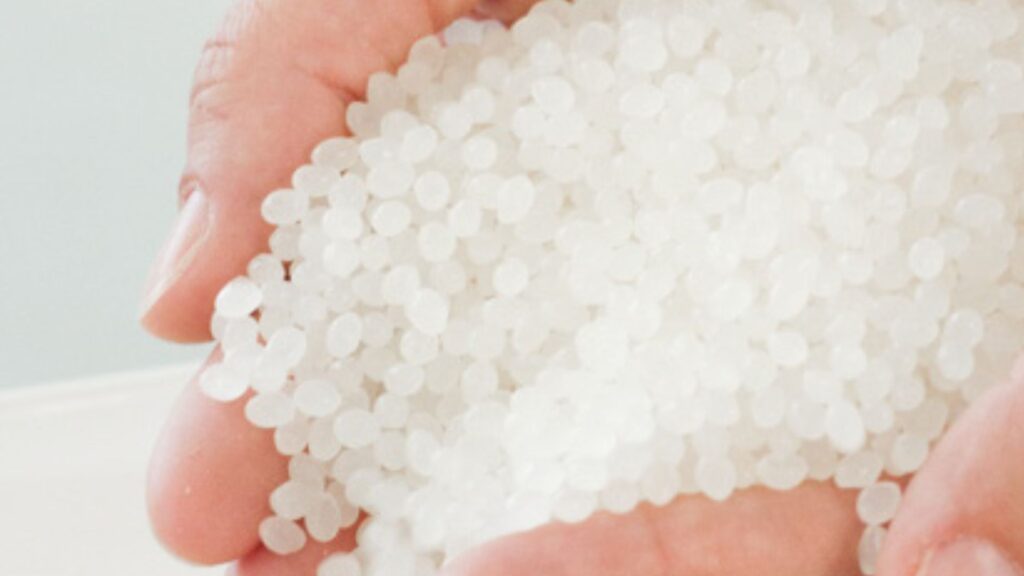

Resin materials used in 3D printing vary depending on the modeling method. Let's take a look at the resin materials that can be used for each molding method.
Resin materials that can be used with thermal melting and laminating (FDM) 3D printers
| Resin material | feature |
| ABS resin | Excellent impact resistance and high mechanical strength |
| PLA Resin | Biodegradable and environmentally friendly |
| ASA resin | Resistant to degradation even outdoors, strength similar to ABS |
| PP resin | Lightweight, durable, and chemical resistant |
| PET resin | Transparent, impact-resistant, recyclable material |
| PETG resin | Improved PET, good balance of chemical resistance and impact resistance |
| polycarbonate | High strength and heat resistance, high transparency |
| Nylon resin | Extremely strong, abrasion resistant, and supple |
| TPU resin | High elasticity, abrasion resistant, flexible |
| TPE resin | Stretches like rubber, soft and unbreakable |
| PS Resin | Light, stiff, and transparent. |
FDM 3D printers mainly use thermoplastic resins such as ABS and PLA resins.
ABS resins are suitable for making functional parts, while PLA resins are used for environmentally friendly products.
ASA resin is suitable for outdoor use, while PETG resin offers a good balance of chemical resistance and impact resistance, making it a material suitable for a wide range of applications.
Resin materials that can be used with optical 3D printers
| Resin material | feature |
| ABS-like resin | Strength, impact resistance, and heat resistance similar to epoxy resins and ABS resins |
| PP-like resin | Epoxy-based resin, PP resin-like properties |
| CMET TSR-821 | Epoxy-based resin, high strength and toughness |
| CMET TSR-829 | Epoxy-based resin, moisture-resistant, high transparency |
| CMET TSR-883 | Epoxy-based resin, ABS-like properties, flame retardant |
| AGILISTA AR-M1 | Acrylic resin, water-resistant |
| EPU (Elastic Polyurethane) | Rubber-like elasticity, retains elasticity over a wide range of temperatures |
| RPU (rigid polyurethane) | Hard and tough, comparable performance to ABS and flame retardant |
| PU (polyurethane) | Rubber-like flexibility and elasticity, abrasion-resistant |
| silicone resin | Flexible, elastic, heat resistant and safe for human body |
| PC (Polycarbonate) | Strong, heat-resistant, lightweight |
Epoxy and acrylic resins are mainly used in the optical molding method.
Typical epoxy-based resins include ABS-like and PP-like resins, which, as their names suggest, have properties similar to those of ABS and PP.
In addition, the high transparency of acrylic resins makes coloring easy, enabling the production of prototypes and figures for design verification.
In addition, materials with rubber-like properties, such as polyurethane (PU) and silicone resin, have been developed in recent years.
With the advent of resins with high toughness, high temperature resistance, and biocompatibility, as well as materials mixed with fillers such as ceramics, the applications of optical 3D printers continue to expand.
How to choose a resin material for 3D printing
Which resin material to choose depends on the product's application and required characteristics.
Select the appropriate material, taking into account the following main points
- strength
- heat-resisting property
- flexibility
- Surface quality
- Chemical Properties
Selecting the right material can improve product performance and reduce costs.
Nevertheless, it can be difficult to select appropriate materials without specialized knowledge and expertise.
Therefore, it is recommended to consult with a specialized contractor for advice on material selection, if necessary.
Summary
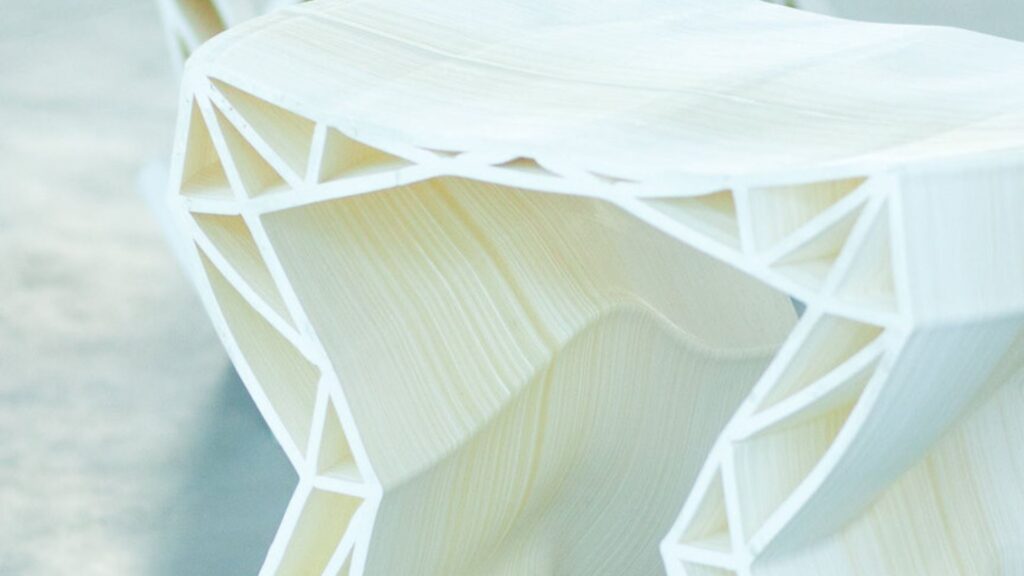

In 3D printing of resins, it is important to understand the characteristics of each molding method and resin material, and to select the method and material that best suits the purpose.
In addition, to achieve high quality modeling, it is necessary to select an appropriate processor.
Working with a vendor with the expertise and experience to produce the ideal product will help you achieve your goals.
If you are considering manufacturing parts using 3D printing, please contact us! Taiga is a free service that allows you to consult with experienced contractors.
We can efficiently proceed with the development of difficult or new parts, small-lot production, prototyping, and mass production while keeping costs low.
For more information about Taiga, click here.
 0120-987-742
0120-987-742