Among the molding methods of 3D printers, "optical molding" has a long history.
This printing method is still widely used for prototype modeling and small-lot production of products.
Nevertheless, there are now a variety of 3D printing methods and options.
Many of you may be asking yourself, "I want to know how light fabrication (LCD) works," or "What is the difference between LCD and other fabrication methods?" What is the difference between LCD and other molding methods?
This article therefore provides a detailed explanation of how optical modeling works, its advantages and disadvantages, and even cautions when using it.
For more information about Taiga, click here.Table of Contents
What is Light Modeling? How it works and its history

Optical modeling is the oldest modeling method among 3D printers.
Laminating is performed by irradiating liquid light-curing resin with a UV light or laser to cure layer by layer.
This results in a highly precise and smooth surface.
Regarding optical modeling technology, Mr. Hideo Kodama of Japan originally applied for a patent in 1980 for a "three-dimensional figure creation device," but the patent was not granted at that time.
Later, in 1986, American Chuck Hull obtained a U.S. patent for the optical fabrication method and established 3D Systems, Inc. to commercialize the world's first optical fabrication 3D printer.
And since the patent expired in 2006, many manufacturers have developed and produced products, and 3D printing technology continues to evolve today.
Difference between optical fabrication and FDM (thermal melting and laminating method)
In addition to optical fabrication, FDM (thermal melting and layering) is another typical fabrication method for 3D printers.
In FDM, thermoplastic resin is melted in a heated nozzle and piled up in layers. The melted material is rapidly cooled and solidified after layering.
Optical modeling, on the other hand, uses light to cure liquid resin.
Optical fabrication provides higher precision and smoother surface finish compared to FDM, while FDM has lower material cost and is suitable for large scale fabrication.
There are three methods of laser fabrication
There are three types of optical imaging: DLP, LCD, and SLA. Let's take a closer look at each of them below.
DLP method
The DLP (Digital Light Processing) method is a 3D modeling technology that uses a projector-like mechanism to irradiate ultraviolet light onto the entire modeling surface at once.
Unlike the method of irradiating one point at a time on a specific spot, it can print in a short time.
Another advantage of the DLP method is that it allows modeling with less material and minimizes resin degradation.
On the other hand, the accuracy tends to become coarser as the modeling area becomes wider, so it is not suitable for modeling large parts.
LCD method
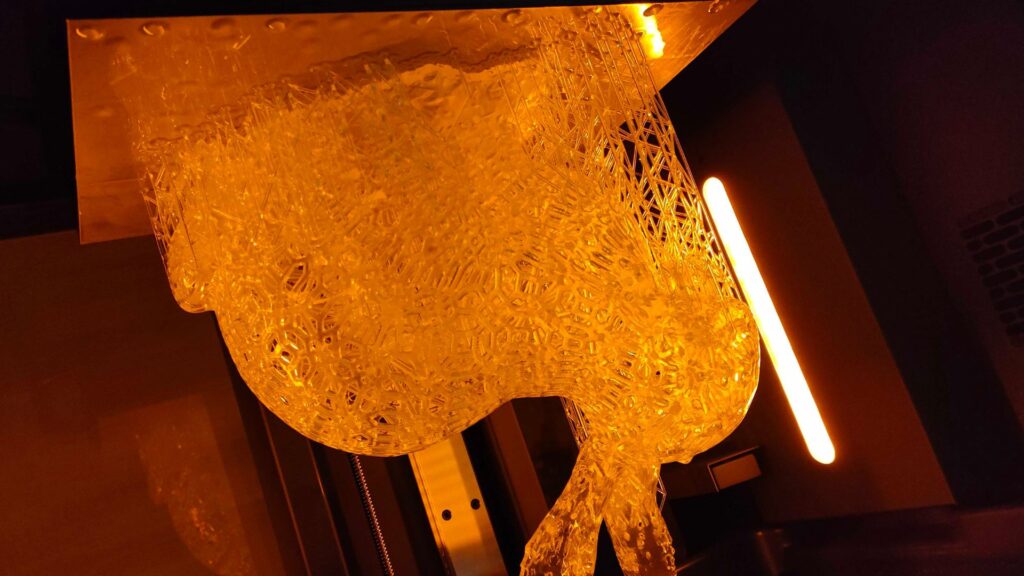

The LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) method, like the DLP method, irradiates ultraviolet rays over a surface, but differs in that it uses a liquid crystal display.
Each pixel of the LCD panel acts as a light mask, allowing the resin to cure individually.
However, it should be noted that LCD panels deteriorate due to heat and ultraviolet rays during molding, requiring periodic replacement and running costs.
Nevertheless, it is suitable for personal use and small-scale manufacturing because of its relatively low cost and high-resolution modeling.
SLA method
The SLA (Stereolithography) method is the most classic optical modeling method that uses a laser to cure resin.
It has the advantage of being able to produce large objects in one piece, but its production speed is somewhat slower than that of DLP and LCD systems.
Another issue is the need to prepare a large number of resins and the deterioration of resins due to long-term storage.
However, printers that solve the issues of molding time and resin degradation have recently been developed using the latest technology.
Advantages of Light Laser Diffraction (LCD)
The advantages of light deposition (LCD) will now be explained.
High-precision modeling is possible.
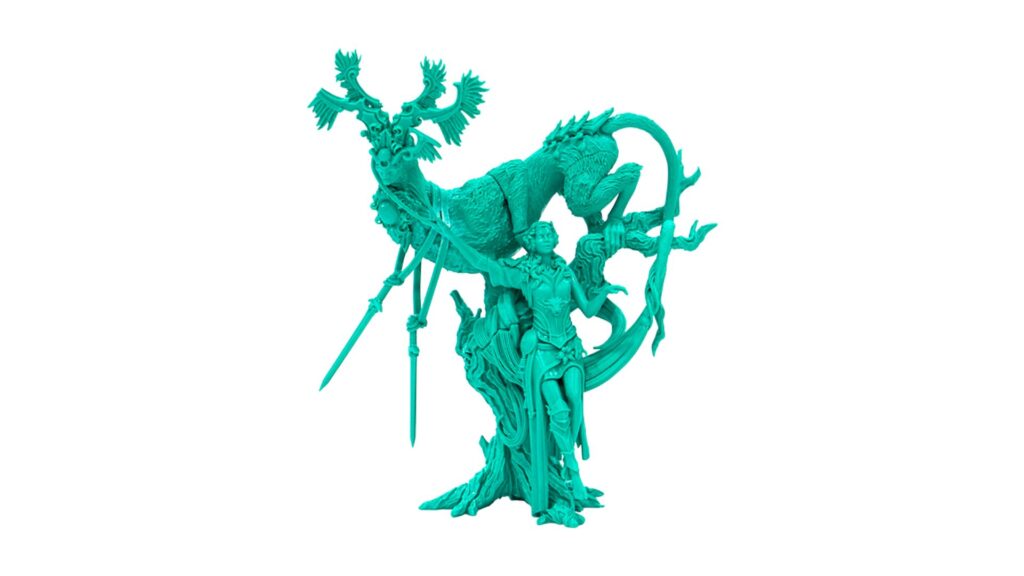

LCD-based optical 3D printers can create objects with extremely high precision.
It can accurately reproduce fine structures and complex shapes, and can also express minute details of 0.5 mm or less.
In addition, since lamination marks are not noticeable and smooth surfaces can be achieved, it can be used in a wide range of situations, from prototypes to final products.
Short molding time
The LCD method cures the entire surface at once, resulting in extremely fast modeling speed.
Since there is no need for point curing as with the conventional SLA method, multiple modeling of large moldings or small products can be performed efficiently.
Can be modeled with a variety of materials
Another advantage of the LCD method is that a variety of light-curing resins can be used.
Materials with a wide range of properties are available, from standard resins to flexible, high-strength, and heat-resistant resins.
The best material would be selected based on the product application and required performance.
Can be used for transparent moldings
LCD-based optical 3D printers can also create transparent models by using a special transparent resin.
This is a major advantage in the development of products where transparency is important, such as optical components, display covers, and models for fluid analysis.
Disadvantages of Light Laser Diffraction (LCD)
The following sections describe each of the disadvantages of optical modeling.
Secondary hardening is necessary in some cases.
In LCD-based optical fabrication, the amount of light received during fabrication varies from part to part, so parts may not be completely cured immediately after fabrication.
Secondary curing treatment to increase strength may require longer production time and additional equipment.
In addition, some secondary curing conditions may affect dimensional accuracy, and appropriate settings must be made according to the type of resin used and the thickness of the modeled object.
Cleaning and treatment of support materials required after molding
LCD-based optical fabrication requires cleaning of uncured resin and removal of support material after fabrication.
In this process, complex shapes are time-consuming to process and may leave marks.
Vulnerable to sunlight and ultraviolet rays
Light-curing resins used in photolithography are generally vulnerable to sunlight and ultraviolet rays.
Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays can cause discoloration and degradation, so consideration must be given when developing products intended for outdoor use or long-term storage.
As a countermeasure, consider using UV protective coatings or special UV-resistant resins.
Materials used in laser fabrication (LCD)
The main material used in photolithography is light-curing resin, which reacts to ultraviolet and visible light to cure.
In resins, a variety of types with different properties have been developed, including standard resins, high-strength resins, flexible and heat-resistant resins, biocompatible resins, etc. Recently, special resins containing ceramics and metal particles have also been introduced.
Scenes in which light laser deposition (LCD) is used
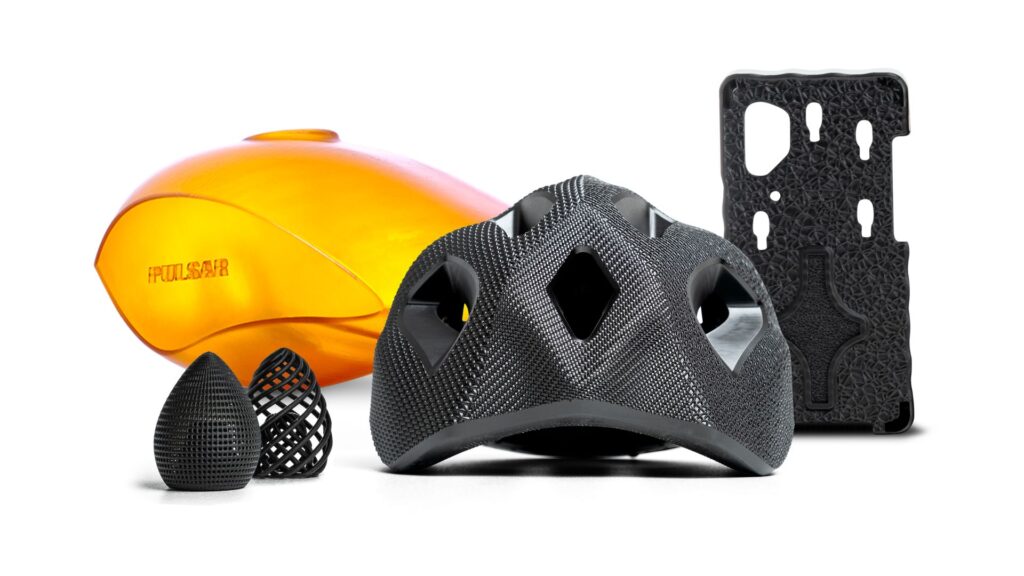

Optical fabrication can be used in a variety of situations due to its high precision and surface quality.
In the medical field, for example, it is used to create patient-specific anatomical models and surgical guides.
In addition, it is also suitable for creating prototypes, manufacturing jigs and tools, making molds, and creating models for lost-wax casting, especially for items that require design and custom-made products.
Flow of 3D printing with light fabrication (LCD)
The general flow of 3D printing with optical fabrication is as follows.
- 3D modeling and data optimization
- Preparation of printer (resin filling)
- molding
- Post-treatment (cleaning and support material removal)
- second hardening
- Finishing
First, 3D data is created using CAD software, and slices are processed by adding support areas.
Next, the resin tank is filled and light is irradiated to create the modeling by repeatedly curing and peeling layer by layer.
After completion, the uncured resin is cleaned, the support material is removed, and secondary curing with UV light and surface treatment are performed if necessary.
What to look out for when 3D printing with light fabrication (LCD)
When performing optical 3D printing, it is important to select the appropriate resin for the application.
The orientation and placement of moldings must be carefully considered because they affect quality and post-processing.
In addition, it is necessary to prevent warpage and deformation in thin-walled or flat shapes, and air bubbles (voids) in thick-walled shapes.
Furthermore, post-processing such as cleaning and secondary effects must be carefully performed because they affect the final quality.
Summary
Optical 3D printers, especially LCD 3D printers, have many advantages such as high precision, high speed modeling, and a wide variety of materials.
While optical fabrication contributes greatly to the efficiency and quality improvement of the product development process, it also has limitations related to the need for post-processing and the characteristics of the material.
Proper equipment selection and operation are essential to obtain high-quality modeling results.
In addition, since in-house implementation requires the training of staff with expertise and the development of facilities, the use of an outside 3D printing service provider may be an option.
If you are considering manufacturing parts using 3D printing, please contact us! Taiga is a free service that allows you to consult with experienced contractors.
We can efficiently proceed with the development of difficult or new parts, small-lot production, prototyping, and mass production while keeping costs low.
For more information about Taiga, click here.
 0120-987-742
0120-987-742