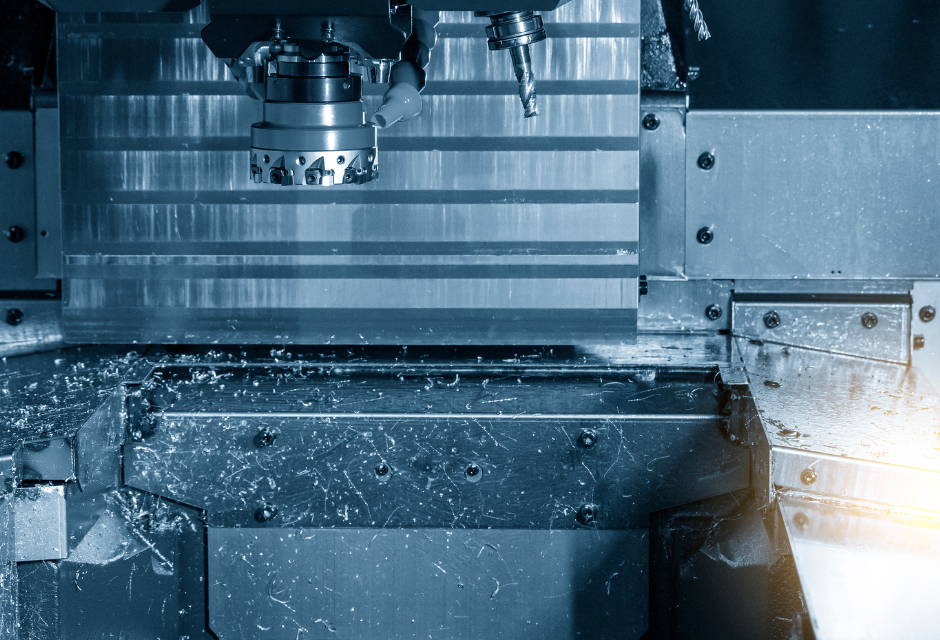

In the manufacturing and production field, the automation and systemization of machine tools is progressing.
In response, an increasing number of companies have introduced machining centers in recent years.
Many of you reading this article are probably wondering about machining processes and machining centers.
In this article, we will explain in detail what machining operations are, how they proceed, and what types of machining centers are available.
For more information about Taiga, click here.Table of Contents
What is machining process?
Machining is a machining process that uses specialized machines to cut and shape metal materials.
Other times it is referred to as milling or machining center machining, but these all refer to the same method.
Machining is generally performed using a specialized machine called a machining center.
Conventional machining centers require machines such as drilling machines and boring machines for milling and drilling, but with a machining center, these operations can be performed with a single machine.
Machining Process Flow
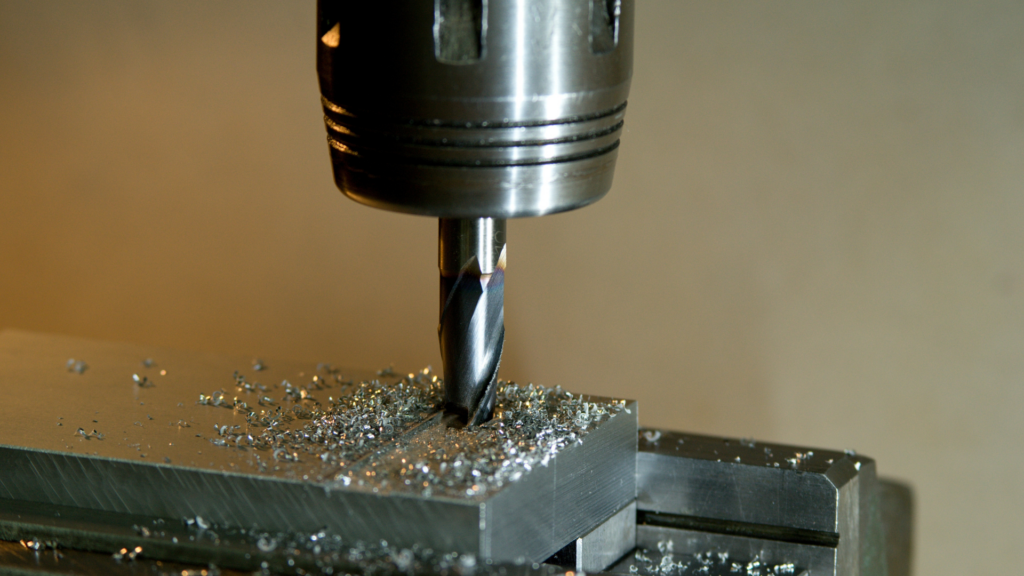

Next, let's take a closer look at the machining process flow.
Step 1: Create a program
In order to perform machining operations, the machining center must be set up.
One of the most important aspects of the program is the creation of the program.
Specifically, numerical data called NC data must be used, which is basically manufactured based on drawings.
However, since the shape information alone is not sufficient for accurate settings, fine adjustments are made to the direction of cutting and the speed at which it is moved.
Programs can be input directly into the machine, but for complex machining, it is recommended to use software such as CAD/CAM for input.
Step 2: Transfer programs
Once the program is produced, it is transferred to the machining center.
To transfer the data, it is necessary to do some work such as converting the data into the language of the machine tool, so please check this in advance to avoid errors and problems.
Step 3: Set materials
Once the program has been produced and transferred, set the material and check the horizontal level.
Fix the material to the machining center using a jig, etc., and set the origin, XYZ axis, and other positions.
The cutting tools are then aligned, measured for shape and length, and after a trial run, the machine is ready for machining.
Step 4: Processing
Cutting oil is sprayed while machining.
Specific processing steps are as follows
- unrefined
- incomplete cut
- bevelling
- Finishing
After checking the dimensions at the end, the machining process is complete.
Types of Machining Centers
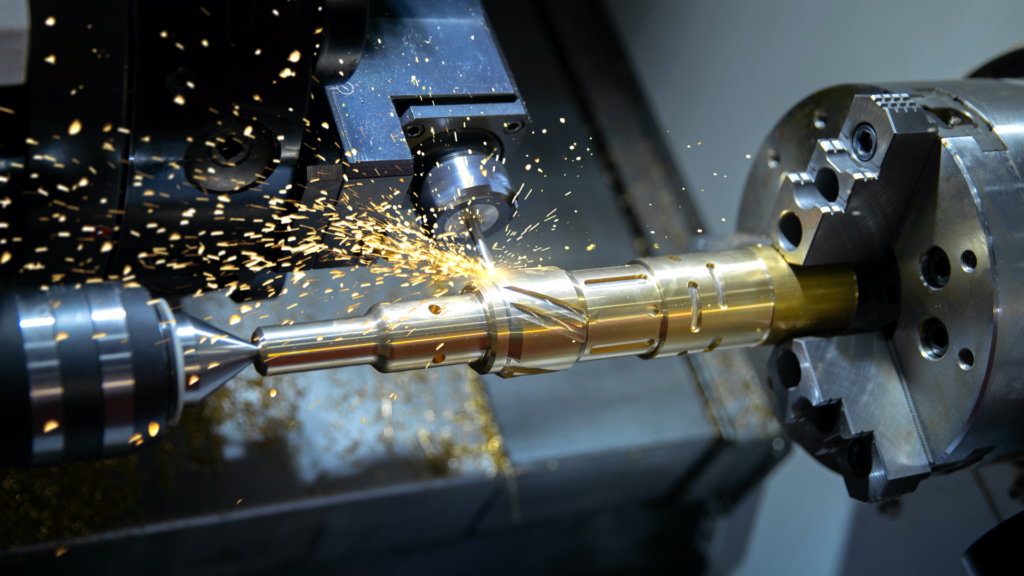

There are several types of machining centers for machining operations.
Below is a detailed look at each of these features.
Vertical Machining Center
Vertical machining centers are used to process materials from above.
The major feature of this machine is that the rotary axis to which the cutting tool is attached is mounted vertically.
Compared to other machines, this machine has the advantage of easy setup and easy-to-use jigs, and has been introduced at many sites.
In addition, the excellent machining accuracy and space-saving design make it easy to install and use in any location.
Horizontal Machining Center
A horizontal machining center is a machine with a horizontally mounted rotary axis to which cutting tools are attached.
Like the vertical machining center introduced earlier, it moves on the XYZ axis, but because the workpiece is machined from the side, the amount of chips discharged is reduced.
In addition, a pallet changer, a device that automatically transfers parts, can be installed, enabling continuous operation for long periods of time.
This makes the machine suitable for mass production.
Gantry Machining Center
A gate-type machining center is a machining center shaped like a gate, and in most cases, not only the Z-axis but also the Y-axis moves as well.
The greatest advantage of the double-column machining center is that there is no limit to the size of the table and large materials can be machined.
5-axis machining center
A 5-axis machining center is a machine with A or B axis and C axis in addition to XYZ axis.
Compared to conventional 3-axis machining centers, more complex machining is possible, which is expected to improve productivity and efficiency.
However, since there are more parts to control, advanced programming knowledge is required to use it.
Basic structure of machining center
Machining centers are extremely complex structures.
Below is a detailed look at the features and roles of the on-board functions.
Role of NC equipment
Machining centers are equipped with systems called NC devices.
This is a computer-controlled system that is responsible for moving the tool precisely according to a built-in program.
NC equipment is the "heart" of a machining center and is a very important system.
ATC Features
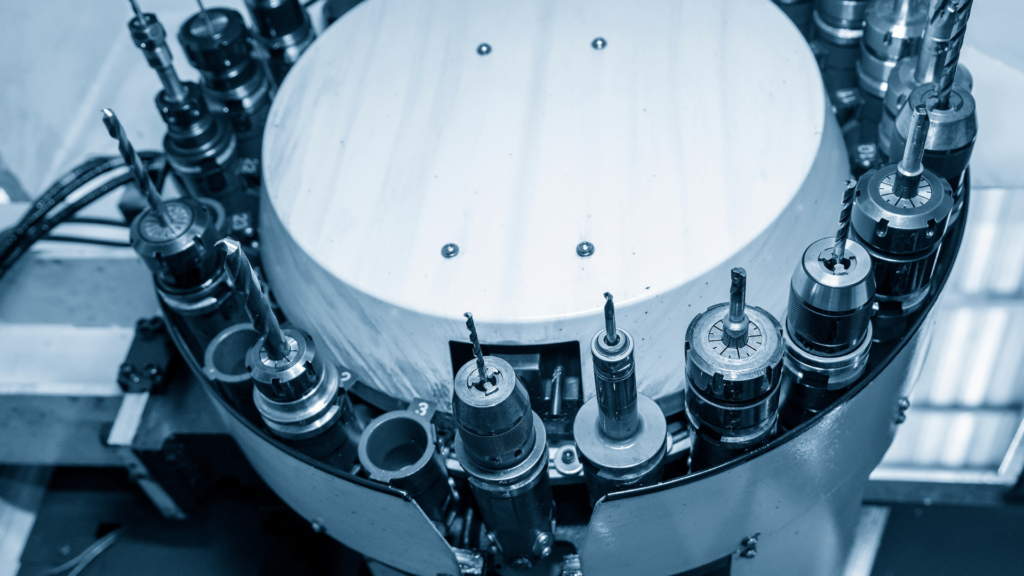
Machining centers are also equipped with ATC functions.
This is an abbreviation for "Automatic Tool Changer," which in Japanese means "automatic tool changer.
ATC makes it easier to shorten processing time and reduce labor costs.
Such ATCs include the following types.
- drum-type
- chain-operated
- magazine style
Bed characteristics
A machining center consists of various elements such as ATCs and index tables.
Among these factors, the bed is the one that has the greatest impact on stability and machining accuracy.
This is the foundation of the machining center and supports the spindle and table.
Such beds require various characteristics such as rigidity and vibration absorption.
There are various types of materials, each with different characteristics, so one must be carefully selected to suit the application and the required processing precision.
Index Table Functions
The index table is an important element that affects the machining accuracy of a machining center.
Specifically, the following functions and roles are performed
- High-precision division
- Automatic indexing function
- Support for rotary machining
- Processing of complex shapes
It is no exaggeration to say that the index table enables machining of complex shapes and multiple faces.
What is the difference between machining centers and other machine tools?
Next, let's take a closer look at the differences between machining centers and other machine tools.
Difference from Lathe
The difference between a machining center and a lathe is in what it rotates.
Unlike a machining center, where the tool rotates, a lathe rotates the material.
In lathe turning, the material is rotated and applied to the cutting tool, which is basically used for machining round bars.
Machining centers can process materials of various shapes because the tool itself rotates.
Difference from Tapping Centers
A tapping center is a machine specialized for "tapping" in the drilling process.
It is mainly used in screw fabrication.
In contrast, machining centers excel in cutting operations.
The tapping function is also available on some machining centers.
Since machining centers are superior in terms of machine precision, careful consideration must be given to which machine to install or use.
Difference from jig borer
Machining centers and jig borers are very similar machines.
It is no exaggeration to say that there is not that much difference in terms of functionality.
However, the jig borer has high vertical machining accuracy.
Jig borers are also used for finishing and are suitable for single piece production.
Nevertheless, jig borers are more difficult to handle than machining centers and can only be used by skilled technicians.
Difference from NC machine tools
The difference between NC machine tools and machining centers lies in tool changeover.
The machining center is equipped with a tool changer for smooth operation.
NC machine tools, on the other hand, require work to be stopped and tools to be changed each time, which in some cases can reduce production efficiency.
If you want to order machining work, "Taiga" is the place to go!
Machining requires advanced skills and knowledge.
A machining center is also required, and if the company does not have the knowledge, skills, or equipment, it must consider outsourcing.
Nevertheless, there are countless suppliers for machining orders, making it difficult to find the right partner for your company.
If this is the case, please use "Taiga".
Taiga is a matching platform in the manufacturing and production industry and serves to connect users and partners.
Not only that, but it also offers a variety of useful functions, such as chat-based communication, drawing editing, and re-purchase functions, which can lead to increased productivity and efficiency.
This service is particularly compatible with high-mix low-volume production, so please feel free to contact us if you are interested.
Summary
Machining is a processing method using a machining center.
In recent years, automation and systemization have increased, and more and more companies are adopting machining centers in line with this trend.
However, machining requires a high level of skill and knowledge, and is not something that can be done casually by beginners.
Therefore, if your company does not have the knowledge, you should consider outsourcing.
By using Taiga, you will be able to find the best partner for your company and smoothly place orders for machining and other operations.
You can create an account for free, so if you are at all curious, please give it a try.
For more information about Taiga, click here.
 0120-987-742
0120-987-742


