
Automobiles and other equipment products are often required to be lightweight for a variety of reasons.
Therefore, many people are considering reducing the weight of the components themselves in order to reduce the weight of equipment, but they may have questions such as "I don't know what materials are suitable for weight reduction" or "I want to know if it is possible to reduce the weight of components without changing the materials.
In this article, we will explain the background behind the demand for lighter products, specific materials that can achieve weight reduction, and how to reduce the weight of parts without changing materials.
Please refer to this section for an explanation of the advantages and cautions for weight reduction of parts.
For more information about Taiga, click here.Table of Contents
Why are products now required to be lighter?
Sustainability efforts are behind the need for lighter weight machinery and equipment.

Currently, countries around the world are promoting efforts to achieve virtually zero greenhouse gas emissions (carbon neutrality) by 2050, with a particular focus on switching from gasoline-powered vehicles to electric vehicles (EVs) that do not emit exhaust gases while driving.
However, because electric vehicles are powered by an electric motor rather than an internal combustion engine, the motor weighs more and has a shorter driving range than gasoline-powered vehicles.
Therefore, the heavier the motor, the lighter the other components must be.
In addition, for fuel-driven equipment such as aircraft and industrial machinery, not to mention automobiles, there is a need to reduce the weight of metal products that serve as components.
In light of these factors, the need for lighter metal products will continue to grow in order to promote carbon neutrality and sustainability.
Five materials that can reduce component weight
One way to reduce the weight of a component is to change the existing material to something else.
Here are five materials, in order, that are effective in reducing the weight of components.
aluminum alloy
Aluminum alloys are metals made from an alloy of aluminum and other metals.
There is a wide range of aluminum alloys, numbered in the 1000 to 8000 range.
Among these, the 2000 series duralumin and super duralumin, alloys of aluminum and copper, and the 7000 series super duralumin, an alloy of aluminum, zinc, magnesium, and copper, are alloys that have the lightweight properties of aluminum with strength comparable to steel materials.
In particular, duralumin is often used for aircraft parts as an alloy with light weight and strength.
Titanium Alloys
Titanium has been widely used as a material for automotive parts because of its light weight and high strength.
In recent years, titanium alloys have been created using lower-cost titanium metal.
Parts made of titanium alloys are utilized as materials for automotive parts such as suspension rods and engine valves to reduce the weight of automobiles.
CFRP (Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastic)
CFRP (carbon fiber reinforced plastic) is a material made by synthesizing carbon fiber and plastic resin.
It combines the toughness and lightweight properties of carbon fiber with the versatility and strength of plastics.
Because of its resistance to corrosion and thermal deformation, it is used in lightweight automobiles, aircraft, and sports equipment, as well as in the space industry.
magnesium alloy
Magnesium alloys are characterized by the lightest weight and highest specific strength of all practical metals, in addition to the easy availability of the material magnesium.
It is also suitable as a material for machining small parts because of its high dent resistance and the smaller dents that occur when materials collide with it compared to aluminum alloys and other alloys.
It also has the greatest vibration absorption of any practical metal, making it an effective material for vibration dampening components such as automobile wheels and steering wheels.
High Performance Resins and Engineering Plastics
High-performance resins and engineering plastics are resin materials that overcome the weaknesses of plastics, which are prone to deformation and cracking at high heat.
Many high-performance resins and engineering plastics have heat resistance temperatures of 100°C or higher and high strength and abrasion resistance.
Because of its light weight and strength, as well as the fact that it does not deform due to heat, it is widely used as a material for automobile and other equipment parts.
How to reduce the weight of parts without changing the material
In some cases, due to material procurement methods and costs, it may be desirable to achieve weight reduction without changing materials.
In such cases, it is possible to reduce weight without changing the existing material by changing the processing method.
The following is a step-by-step explanation of how to reduce the weight of components without changing existing materials.
Change the shape to a walled-out, hollow structure
Means of weight reduction include design modification to reduce the product's wall thickness or to a hollow structure.
By adding more holes in the design stage and by adding cavities in the structure, it is possible to reduce weight while maintaining the product's material.
However, the strength and rigidity of the product may be reduced by removing the wall or hollowing out the structure.
The design will be required to ensure the necessary strength and rigidity, taking into consideration the application of the component and the environment in which it will be used.
Thinning and plate thickness changes
Thinning or changing the thickness of the plate is one way in which weight reduction can be achieved with little or no change to the structure of the component.
There is also the advantage of not having to make design changes, etc., and of being able to easily understand the issues and weaknesses of the part at the time of design. However, the disadvantage is that the processing methods that can be used for weight reduction are limited, such as casting, die casting, and resin molding for thin-walled parts, and can manufacturing and sheet metal working for plate thickness changes.
Advantages of Reducing Part Weight
Reducing component weight provides the following benefits
- Improved fuel efficiency of products
- Performance Improvements
- Longer component life
First, weight reduction of components improves the fuel efficiency of the product.
For example, a car that weighs less will require less energy to run and will therefore be able to travel more distances on the same amount of fuel.
Also, weight reduction can be expected to improve the performance aspect of the product.
For example, the heavier the car, the greater the centrifugal force acting on it when it goes around a curve.
Conversely, the lighter the weight of the vehicle, the smaller the centrifugal force will be, and the turning and maneuverability of the vehicle will be greatly enhanced.
In addition, lighter components will also slow down the deterioration and wear of the components themselves.
This is because stopping a heavy automobile requires greater wear and tear on brake pads and tires, but if the automobile is lighter, the wear and tear on each component will be smaller.
Points to keep in mind when reducing component weight
While weight reduction of components has many advantages, it also has disadvantages.
Cost increases due to changes in materials and processing methods
Changing materials and processing methods to reduce weight often results in higher costs.
Consider that lighter weight will result in less durability and more frequent replacement, which will increase costs.
Decrease in durability, comfort, etc.
Weight reduction may reduce the durability of components.
In particular, parts with a lot of ground contact surfaces, such as automobile wheels, may not be able to ensure the performance and safety of the automobile itself due to weight reduction.
Lightweighting can compromise quieting features and cause noise when driving a car.
Advantages of using 3D printing process to reduce component weight
When considering the manufacture or fabrication of lightweight components, 3D printers are an effective tool.
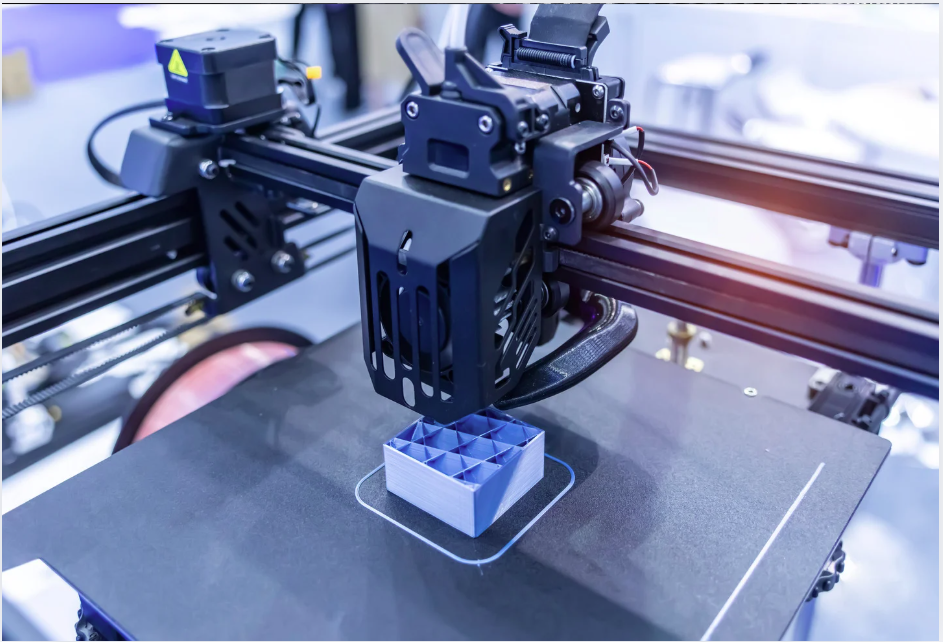
By utilizing a 3D printer, prototyping and small-lot production of parts can be realized in a short period of time and at low cost from 3D data created with 3D CAD.
Since the company can handle both resin and metal materials, it can create parts from resin materials, and can also handle mass production by making simple metal molds.
3D printers are particularly suited for creating parts to meet the needs of customers with short delivery times and frequently changing specifications.
Summary
Materials effective for weight reduction of parts, methods to achieve weight reduction, and advantages and cautions for weight reduction were explained.
From the perspective of achieving carbon neutrality and other factors, the need for lighter components is expected to increase in the future.
While taking into account issues such as design changes and increased costs, consider creating the parts with a 3D printer to reduce the weight of the parts.
Considering manufacturing or machining lightweight components?Taiga."Taiga is a free service that allows you to consult with experienced contractors.
We can efficiently proceed with the development of difficult or new parts, small-lot production, prototyping, and mass production while keeping costs low.
For more information about Taiga, click here.
 0120-987-742
0120-987-742


