In recent years, microfabrication has been increasingly used in the manufacture of medical devices.
This article will provide an overview of microfabrication in medical device manufacturing, as well as the techniques and methods of microfabrication.
Examples of typical medical devices manufactured by microfabrication will also be introduced for your reference.
For more information about Taiga, click here.Table of Contents
What is microfabrication?
Microfabrication is a technology that uses equipment such as machining centers and electrical discharge machines to perform high-precision processing.

Microfabrication can achieve finer machining than precision machining, which is a similar term.
Why is microfabrication necessary in medical devices?
Microfabrication is used as a processing technology for electronic, semiconductor, and optical products that require precision in the micron and nanometer range.
In recent years, microfabrication has been increasingly employed in medical device manufacturing.
This is because microscopic dimensional control has made it possible to manufacture medical devices that cannot be achieved with conventional machining in microfabrication.
Furthermore, microfabrication leads to the reduction of wasted materials and processes, and is therefore attracting attention in terms of cost reduction and efficiency in medical device manufacturing.
Major technologies and methods of microfabrication for medical applications
Major microfabrication techniques and methods suitable for medical device manufacturing are described in order.
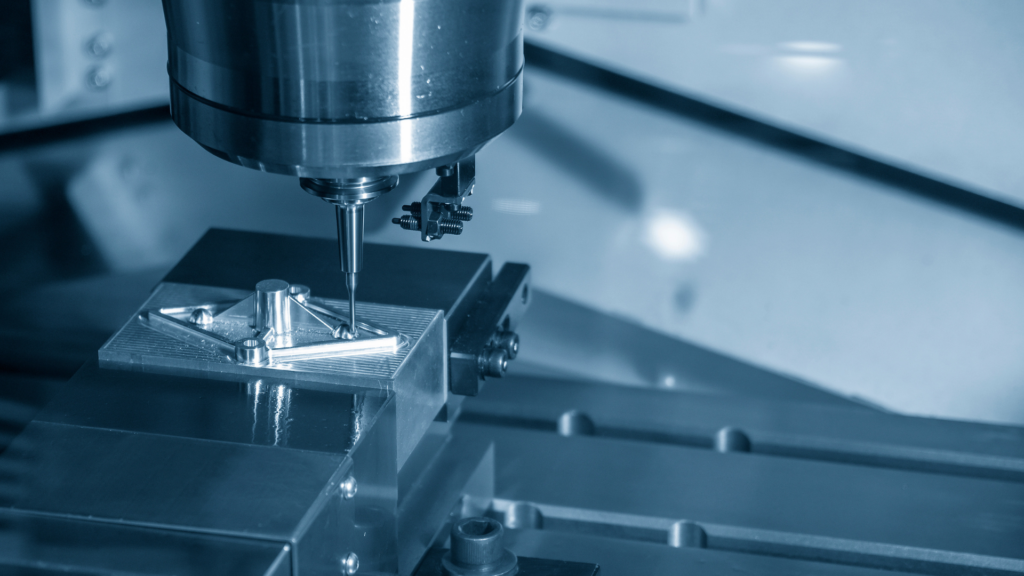
Micro machining (ultra-precision cutting)
Micromachining is a technology that uses a machining center to create complex three-dimensional structures on a substrate, and there are two main types: surface micromachining and bulk micromachining.
Surface micromachining is a method of creating three-dimensional structures on a substrate as if layers are stacked on top of each other.
It is mainly used in the manufacture of integrated MEMS with electronic circuits in semiconductors.
Bulk micromachining is a method of creating various structures by deeply cutting wafers.
While it offers a high degree of freedom in processing, it has the disadvantage of easily damaging the workpiece.
electrical discharge machining
Electrical discharge machining is a technology that achieves microscopic processing by means of electrical discharge.
There are two main types of EDM: wire EDM and die-sinking EDM.
Wire electrical discharge machining is a method of cutting and processing complex shapes by means of an extremely thin wire.
It is mainly employed in the manufacture of precision parts for aircraft and automobiles.
Die-sinking electric discharge machines use electrodes to process dies while melting the material.
It is mainly used in mold and tool manufacturing.
By combining wire EDM and die-sinking EDM, more precise and complex parts can be machined.
Laser Microfabrication
Laser microfabrication is a microfabrication technique that uses short-pulse lasers such as femtolasers.
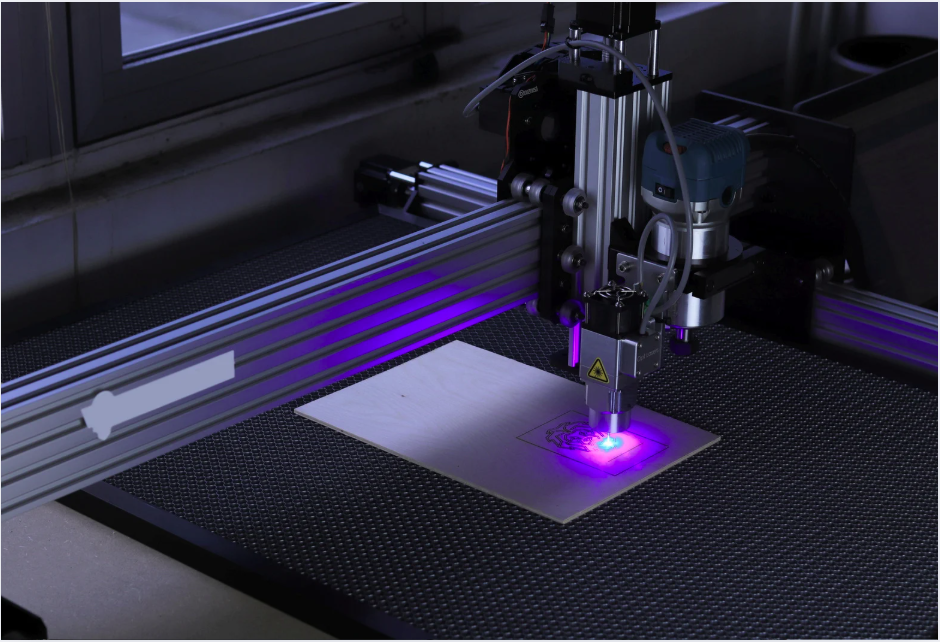

High-precision, non-contact precision machining can be achieved while minimizing thermal effects on the material.
Since physical abrasion does not occur during processing, the advantage is that fine holes and grooves can be processed even in fragile materials such as glass and ceramics.
It is also suitable as a processing method for medical device manufacturing because it is easy to maintain accuracy even when processing complex shapes.
Microfabrication by 3D printing
This method utilizes 3D printers that can handle microfabrication and precision processing at the micro-nano level.
3D printers that use stacked modeling can also create complex shapes such as hollow structures.
Another advantage is that the output is accurate from CAD data, so it is not affected by the technical level of the engineer performing the processing, and microfabrication can be performed with stable quality.
Examples of medical materials and products that can be handled by microfabrication
When considering microfabrication for medical devices, it is also important to select the appropriate material for each product.
Here we introduce the main materials used in medical devices and examples of actual products.
Titanium Alloy|Implants and Orthopedic Devices
Titanium is a lightweight and strong material.
It is resistant to corrosion and is less likely to be rejected when inserted into the body.
It is used as a material for implants, artificial joints, bone fixation plates, and other orthopedic devices that touch the body, as well as for MRI and CT scans.
Stainless steel|Surgical tools and needles
Stainless steel is a material widely used in medical equipment because of its high corrosion resistance and ease of keeping clean.
Because they can withstand repeated high-pressure steam sterilization, they are used in medical devices that are inserted into the body with high frequency, such as surgical instruments, forceps, and needles.
PEEK|Catheters & Surgical Parts
PEEK (polyetheretherketone) is a crystalline resin with a high glass transition temperature.
The high strength and rigidity of the product allows it to maintain stable quality even under high loads, high-friction conditions, and high temperatures up to approximately 250°C.
Because of its high resistance to chemicals and solvents, it is widely used as a material for dental materials such as prosthetic materials and implant abutment materials, as well as for catheters and surgical parts.
Ceramics|Dental and Artificial Joint Parts

Ceramics are inorganic compound materials that combine metallic and non-metallic elements, such as oxides and carbides, with materials composed of non-metallic elements, such as silicon and diamond.
By combining various elements, a wide range of ceramics can be created.
Ceramics, which are resistant to heat and corrosion, are used as materials for dental materials and artificial joint components.
Examples of major medical products manufactured by microfabrication
The following are examples of major medical devices manufactured by microfabrication.
implant (esp. dental)
The surfaces of medical implants are microfabricated.
The microfabrication of the surface increases the bonding area where the implant body contacts the alveolar bone, which makes it easier to bond with the bone, thereby increasing stability.
Another advantage is that the larger bonding area distributes the impact on the implant body that occurs when chewing, reducing the burden on the alveolar bone.
surgical instrument
Microfabrication is also utilized in the manufacture of surgical instruments such as tweezers, forceps, and surgical scissors.
For example, laser microfabrication is used in the manufacture of stents.
Laser processing is used to attach markers for contrast and surface finishing.
Other microfabrication processes are used to achieve high-precision dimensions, thereby enhancing the performance and safety of surgical instruments.
Medical device parts
Parts used in medical devices, such as pumps and valves, are also manufactured by microfabrication.
For example, stainless steel pipes have tiny holes drilled into them by microfabrication.
Quality control and certification required for medical microfabrication
Medical devices are for use on the human body.
To ensure safety and quality, quality control and certification are required for medical microfabrication.
Quality control and certification required for medical microfabrication will be explained.
ISO/GMP
ISO 13485" and GMP are quality standards for the design and manufacture of medical devices.
ISO 13485 is an international quality management system standard for medical devices, established to maintain the safety and quality of medical devices.
GMP is an abbreviation for "Good Manufacturing Practice," which refers to standards for manufacturing and quality control.
Pharmaceutical GMP" has been established as a standard that defines the manufacturing and quality control of medical products from the purchase of raw materials to shipment.
If you are developing a medical business, including medical device manufacturing, you will need to obtain ISO 13485 and pharmaceutical GMP.
traceability
Traceability is a system that enables the tracking of the lifecycle flow of pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and medical materials used in the medical field, from manufacture, distribution, dose, use, and disposal.
By building traceability, the lifecycle of a medical site can be tracked, and if a problem should occur, it can be instantly determined which phase is at fault.
Summary
Microfabrication techniques in medical device manufacturing, materials used, and precautions during processing were explained.
The use of microfabrication enables the manufacture of medical devices with higher precision and assures safety and quality.
However, it is also necessary to obtain the necessary quality control and certification for production.
When requesting microfabrication for medical device manufacturing purposes, be sure to choose a supplier that not only has advanced technology, but also has the necessary quality control and certification.
If you are considering manufacturing sensitive components, please contact us.Taiga."Taiga is a free service that allows you to consult with experienced contractors.
We can efficiently proceed with the development of difficult or new parts, small-lot production, prototyping, and mass production while keeping costs low.
For more information about Taiga, click here.
 0120-987-742
0120-987-742

